This document provides a comprehensive comparison between traditional advertising methods and digital advertising strategies. It explores the key differences in reach, cost, targeting, measurability, and engagement, highlighting the strengths and weaknesses of each approach. The aim is to provide a clear understanding of which advertising method is best suited for different business needs and marketing objectives.
Introduction
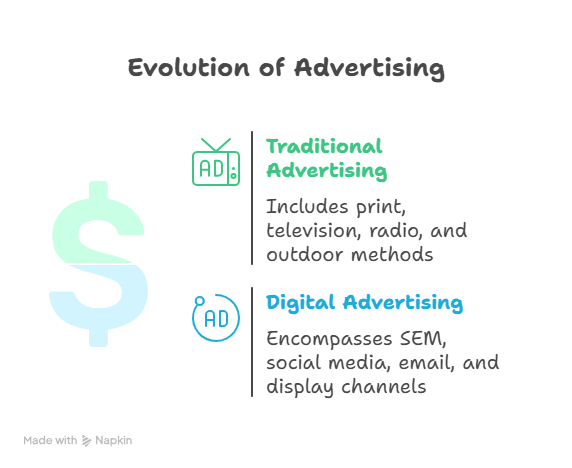
Advertising has evolved significantly over the years. Traditional advertising, which includes methods like print, television, radio, and outdoor advertising, has been a mainstay for decades. However, the rise of the internet and digital technologies has led to the emergence of digital advertising, encompassing channels like search engine marketing (SEM), social media advertising, email marketing, and display advertising. Both traditional and digital advertising have their own unique advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between them depends on various factors, including target audience, budget, and marketing goals.
Reach
Traditional Advertising:
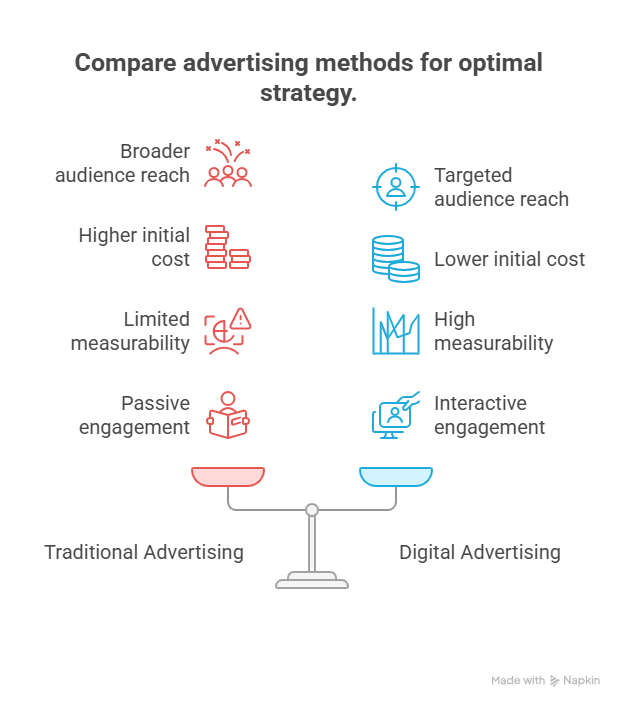
- Mass Audience: Traditional advertising typically reaches a broad, undifferentiated audience. For example, a television commercial during a popular show can reach millions of viewers.
- Geographic Limitations: While national campaigns are possible, traditional advertising often has geographic limitations. Local newspapers and radio stations primarily reach audiences within a specific region.
- Passive Exposure: Viewers and listeners are often passively exposed to traditional ads, meaning they may not be actively seeking the information.
Digital Advertising:
- Global Reach: Digital advertising has the potential to reach a global audience, as the internet transcends geographic boundaries.
- Niche Audiences: Digital channels allow for targeting niche audiences based on demographics, interests, and online behavior.
- Active Engagement: Users often actively engage with digital ads, such as clicking on a link or watching a video.
Cost
Traditional Advertising:
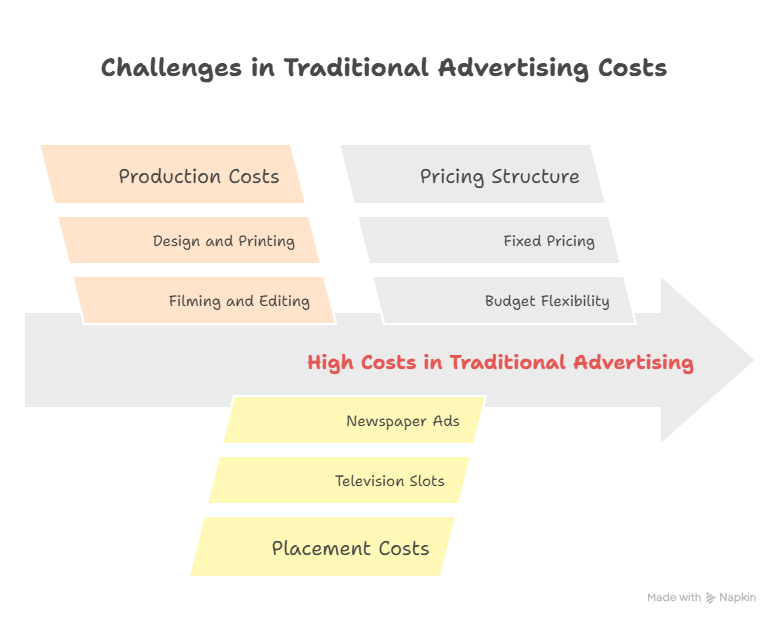
- High Production Costs: Creating high-quality traditional ads, such as television commercials or print ads, can be expensive due to production costs, including filming, editing, and design.
- High Placement Costs: Securing prime advertising slots, such as during popular television shows or in widely circulated newspapers, can be very costly.
- Fixed Pricing: Traditional advertising often involves fixed pricing, making it difficult to adjust budgets based on performance.
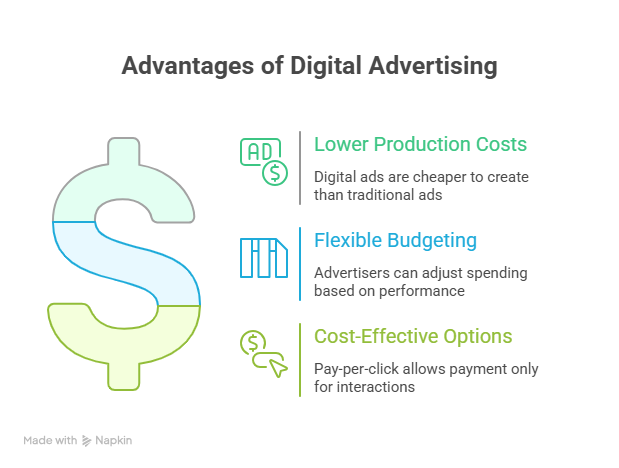
Digital Advertising:
- Lower Production Costs: Digital ads can often be created at a lower cost compared to traditional ads, especially for channels like social media and email marketing.
- Flexible Budgeting: Digital advertising platforms allow for flexible budgeting, enabling advertisers to adjust spending based on performance and ROI.
- Cost-Effective Options: Options like pay-per-click (PPC) advertising allow advertisers to pay only when users interact with their ads.
Targeting
Traditional Advertising:
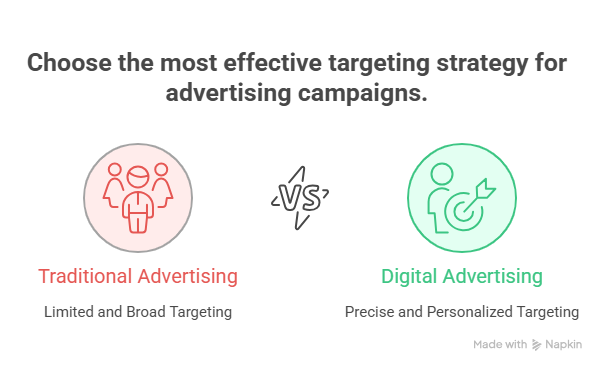
- Limited Targeting: Traditional advertising offers limited targeting options, relying primarily on demographic data and geographic location.
- Broad Demographics: Advertisers often target broad demographic groups, such as adults aged 25-54, without the ability to refine their targeting further.
- Indirect Targeting: Targeting is often indirect, based on the audience profile of the media channel rather than individual user characteristics.
Digital Advertising:
- Precise Targeting: Digital advertising enables precise targeting based on a wide range of factors, including demographics, interests, online behavior, purchase history, and location.
- Behavioral Targeting: Advertisers can target users based on their past online behavior, such as websites visited, products viewed, and searches performed.
- Personalized Messaging: Digital advertising allows for personalized messaging, tailoring ads to individual users based on their specific interests and needs.
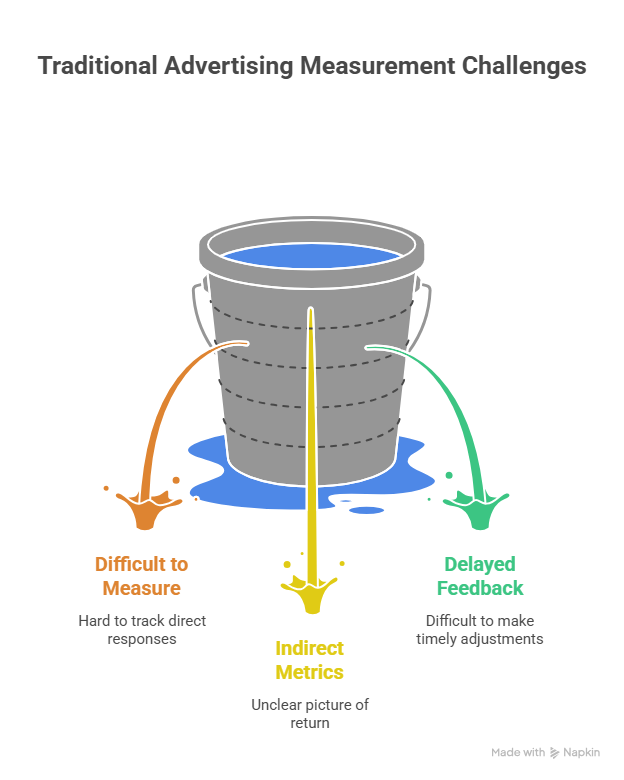
Measurability
Traditional Advertising:
- Difficult to Measure: Measuring the effectiveness of traditional advertising can be challenging, as it is difficult to track direct responses and attribute sales to specific ads.
- Indirect Metrics: Metrics like reach and frequency are often used to estimate the impact of traditional advertising, but they do not provide a clear picture of ROI.
- Delayed Feedback: Feedback on traditional advertising campaigns is often delayed, making it difficult to make timely adjustments.
Digital Advertising:
- Highly Measurable: Digital advertising provides detailed metrics and analytics, allowing advertisers to track the performance of their campaigns in real-time.
- Direct Response Tracking: Advertisers can track direct responses to digital ads, such as clicks, conversions, and sales.
- Real-Time Optimization: Real-time data allows advertisers to optimize their campaigns on the fly, improving performance and ROI.
Engagement
Traditional Advertising:
- Passive Engagement: Traditional advertising often involves passive engagement, with viewers or listeners simply being exposed to the message.
- Limited Interaction: Opportunities for interaction are limited, typically involving call-to-actions like visiting a store or calling a phone number.
- One-Way Communication: Traditional advertising is primarily a one-way communication channel, with limited opportunities for feedback or dialogue.
Digital Advertising:
- Interactive Engagement: Digital advertising encourages interactive engagement, with users able to click on ads, watch videos, share content, and leave comments.
- Two-Way Communication: Digital channels facilitate two-way communication, allowing advertisers to engage with their audience, respond to questions, and gather feedback.
- Personalized Experiences: Digital advertising can create personalized experiences, tailoring content and offers to individual users based on their preferences.
Strengths and Weaknesses
| Feature | Traditional Advertising | Digital Advertising |
| —————– | ——————————————————– | ——————————————————— |
| Reach | Broad, mass audience; geographic limitations | Global reach; niche audiences |
| Cost | High production and placement costs; fixed pricing | Lower production costs; flexible budgeting; cost-effective |
| Targeting | Limited targeting; broad demographics | Precise targeting; behavioral targeting; personalization |
| Measurability | Difficult to measure; indirect metrics; delayed feedback | Highly measurable; direct response tracking; real-time optimization |
| Engagement | Passive engagement; limited interaction; one-way communication | Interactive engagement; two-way communication; personalized experiences |
| Strengths | High credibility; strong brand building | Highly targeted; measurable; cost-effective |
| Weaknesses | High cost; limited targeting; difficult to measure | Can be intrusive; requires constant monitoring and optimization |
Conclusion
Both traditional and digital advertising have their own unique strengths and weaknesses. Traditional advertising can be effective for building brand awareness and reaching a broad audience, while digital advertising offers precise targeting, measurable results, and cost-effective options. The best approach depends on the specific goals and resources of the advertiser. In many cases, a combination of both traditional and digital advertising strategies can be the most effective way to reach a target audience and achieve marketing objectives.

888starz uz, O’zbekistondagi online o’yinlar uchun afzal sayt qimor o’ynash uchun ideal imkoniyatlar taqdim etadi. Bu onlayn kazino turli o’yinlar, bonuslar va qiziqarli aktsiyalar bilan to’la.
888starz uz saytiga kirish juda oson . O’yinchilar o’z hisoblarini osonlik bilan yaratib, o’yinlarga kirishlari mumkin.
Har haftada yangi bonuslar va aktsiyalar taqdim etiladi . Bu esa o’yinchilarning qiziqishini yanada kuchaytirishga yordam beradi .
888starz uz saytida o’yinchilarning xavfsizligini ta’minlash juda muhim hisoblanadi. Ular o’z foydalanuvchilarining ma’lumotlarini himoya qilish uchun zamonaviy usullarni qo’llaydi .
скачать бк 888starz скачать бк 888starz